Planter Box

Infiltrating planter box designed to capture and treat rooftop runoff (Plymouth, MA).
Description
Planter boxes are bioretention treatment control measures that are completely contained within an impermeable structure with an underdrain (they do not infiltrate). The boxes can be comprised of a variety of materials, such as brick or concrete, (usually chosen to be the same material as the adjacent building or sidewalk) and are filled with gravel on the bottom (to house an underdrain system), planting soil media, and vegetation. As stormwater (typically roof runoff conveyed via a downspout) passes down through the planting soil, pollutants are filtered, adsorbed, and biodegraded by the soil and plants.
General Cost Considerations
Estimated cost range for planter boxes is $24 to $32 per square foot.
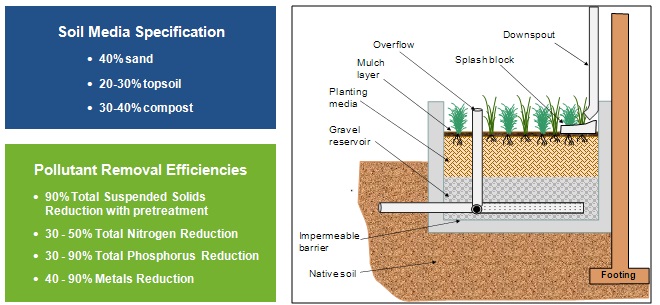
Illustration of a planter box. Adapted from the Bayou Land RC&D BMP Guidance Document.
Design Considerations
Note: For more detailed design guidance, refer to the Massachusetts Stormwater Handbook.
- Design at a minimum to capture and treat the required water quality volume
- Planter boxes are typically designed in layers as follows (bottom to top):
- Concrete or brick planter box, lined with impermeable geomembrane to prevent infiltration near the building foundation
- Minimum 12 inch gravel layer with underdrain, which shall be slotted, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipe
- Minimum depth of 2 to 3 feet of soil media (see specification) to provide sufficient root zone for plant palette
- 2 to 3 inches of mulch
- Maximum of 6 inches of ponding above the mulch
- Overflow riser shall be plumbed to underdrain
Construction Considerations
- Provide energy dissipation (e.g., splash block) at each concentrated inlet point
- The use of treated wood or galvanized metal anywhere within the planter box should be avoided
- Material of planter boxes should be selected carefully to blend in and enhance aesthetics of adjacent structures (buildings and sidewalks)
- Plants should be selected carefully to minimize maintenance and function properly. Native plant species and/or hardy cultivars are preferred
Maintenance
- Inspect for erosion and repair areas
- Remove accumulated fine sediments, dead leaves and trash to restore surface permeability
- Eradicate weeds and prune back excess plant growth that interferes with facility operation
- Periodically observe function under wet weather condition