Bank Shaping and Vegetating
Adapted from Water Related Best Management Practices in the Landscape (Mississippi State University, 1999)
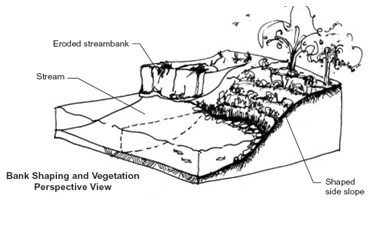
Description
Bank shaping involves excavating and filling the raw, eroded stream bank to create a side slope which is suitable for the site. Suitability criteria include soil materials, moisture conditions, planned vegetation, bank loading conditions, and hydraulic exposure of the site. Appropriate plant materials are selected and installed to stabilize the side slope.
Applicability
This technique is primarily used as one of the least intensive approaches to restoration of bank erosion, and is often a preparatory step for other bank stabilization techniques. The bank to be shaped must not currently be experiencing mass movement.
Design Considerations
Materials
- Select native plant materials that are suited to the velocity regime and other site conditions or have shown success along other, neighboring, similar stream reaches.
- Lower slope segments can be planted with flood tolerant species while upland species may be more suited for the better drained, upper slope.
- Select species which will bend during flow, and will withstand ice loading and abrasion. On dry sites, choose species which can root to the available groundwater level.
- Proper design by a professional river engineer is critical, particularly with regard to the location of the bankfull elevation of the stream.
Installation
- Schedule shaping work to end during the planting windows for the selected vegetation and to occur during periods which will not interfere with key aquatic species reproduction.
- Divert flow away from the stream bank and install silt fences or other devices to keep construction generated sediment from entering the stream.
- Salvage topsoil for applying to the slope surface as a planting medium.
- Plant, seed, fertilize, and mulch according to recommendations.
- Follow with periodic supplemental water if needed to assure establishment.
References
MSU. 1999.
Water Related Best Management Practices in the Landscape. Mississippi State University-Center for Sustainable Design.